The $7 Trillion Question: Will AI Agents Make Human Workers Obsolete by 2030

🤖 The AI Revolution Is Already Here!
Imagine walking into your office in 2030. Your AI assistant has already analyzed overnight market trends, drafted responses to client emails, and scheduled your meetings for maximum productivity. It's generated preliminary designs for your next product launch and identified three potential supply chain issues—all before you've had your morning coffee.
Is this a productivity paradise or the beginning of the end for human workers?
According to McKinsey, AI technologies could automate work activities that currently absorb $7 trillion in wages globally. This staggering figure has business leaders, economists, and workers asking the same urgent question: Will AI agents replace human workers by 2030?
The answer isn't simple. While AI agents are rapidly changing how we work, the future won't be defined by complete replacement but by complex transformation. Let's explore what this means for your business and workforce.
Understanding AI Agents and Their Capabilities
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are software systems that can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional software that follows explicit instructions, AI agents can:
- Learn from experience
- Adapt to new situations
- Work autonomously with minimal human oversight
- Process natural language and understand context
- Perform complex reasoning tasks
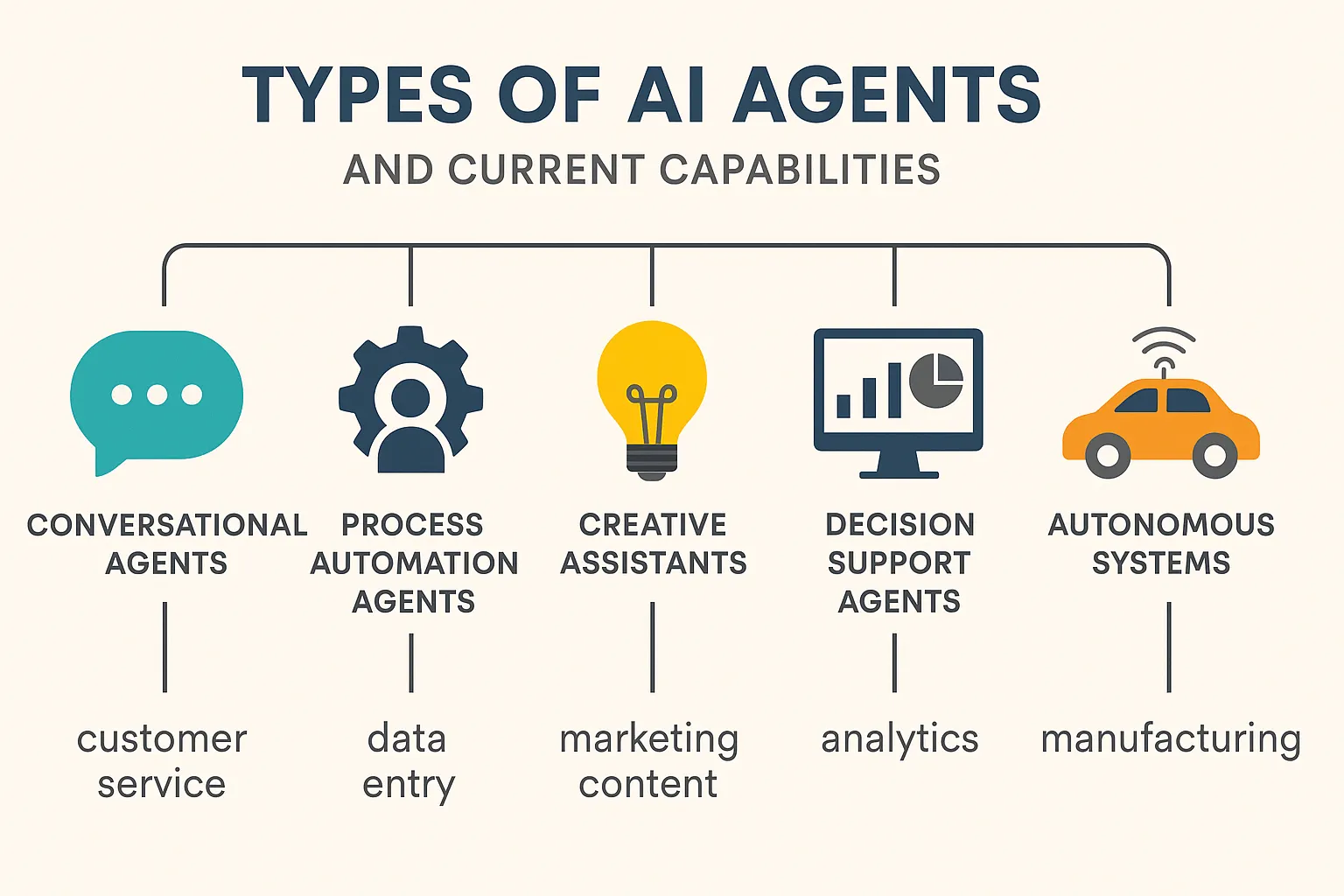
Types of AI Agents Transforming Work
Type of AI Agent Current Capabilities Business Applications Conversational Agents Customer service, information retrieval, basic problem-solving Customer support, internal helpdesks Process Automation Agents Document processing, workflow management, data entry Back-office operations, compliance, finance Creative Assistants Content generation, design suggestions, editing Marketing, product development Decision Support Agents Data analysis, pattern recognition, prediction Strategy, risk management, forecasting Autonomous Systems Independent task execution, physical operations Manufacturing, logistics, security "AI won't replace workers—but workers using AI will replace those who don't." — Erik Brynjolfsson, Stanford Digital Economy Lab
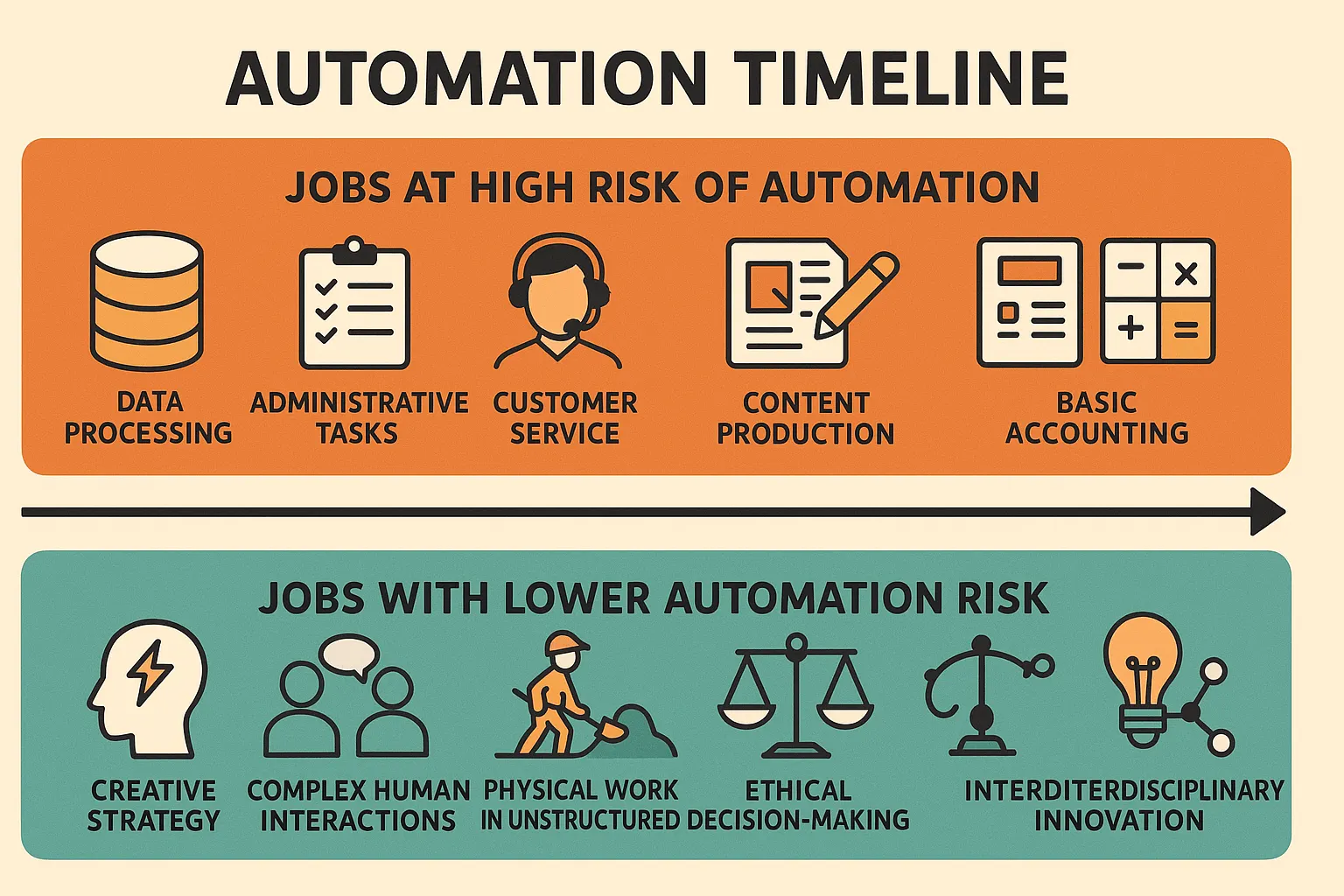
The Automation Timeline: What to Expect by 2030
📊 Jobs at High Risk of Automation
- Data Processing Roles: Data entry, basic analysis, and reporting functions
- Administrative Tasks: Scheduling, document management, basic correspondence
- Customer Service: Routine inquiries, basic support functions
- Content Production: Basic writing, editing, and content curation
- Basic Accounting: Bookkeeping, transaction processing, basic tax preparation
🛡️ Jobs With Lower Automation Risk
- Creative Strategy: Original concept development, innovative problem-solving
- Complex Human Interactions: Negotiation, emotional support, leadership
- Physical Work in Unstructured Environments: Construction, maintenance in variable settings
- Ethical Decision-Making: Situations requiring moral judgment and cultural sensitivity
- Interdisciplinary Innovation: Work requiring cross-domain knowledge and novel combinations
The Economic Impact: Beyond Job Replacement
The economic implications of AI agents extend far beyond simple job displacement. Here's what business leaders need to understand:
Productivity Gains and New Value Creation
AI agents are expected to add $13-15 trillion to global GDP by 2030, according to PwC. This comes from:
- Efficiency improvements: Reducing time spent on routine tasks
- Error reduction: Minimizing costly mistakes in processes
- 24/7 operations: Enabling continuous business processes
- Scalability: Handling volume increases without proportional cost increases
The Redistribution Effect
Rather than eliminating jobs entirely, AI will often redistribute work:
- Task automation ≠ job elimination
- Many roles will be augmented rather than replaced
- New jobs will emerge to manage AI systems
- Human-AI collaboration will create hybrid roles
Small Business Impact
For startups and SMEs, AI agents present unique opportunities and challenges:
- Democratization of capabilities: Access to tools previously available only to large enterprises
- Competitive leveling: Ability to compete with larger organizations through AI-enhanced productivity
- Lower barriers to entry: Reduced need for large workforces to deliver value
- Adaptation challenges: Need for rapid skill development with fewer resources than large companies
AI Agents and Job Automation: The Human Factor
Skills That Will Remain Valuable
As AI capabilities expand, certain human skills become more—not less—valuable:
- Critical Thinking: Evaluating information, questioning assumptions, making judgment calls
- Creative Problem-Solving: Finding novel solutions to complex challenges
- Emotional Intelligence: Understanding human needs, motivations, and concerns
- Ethical Reasoning: Making value-based decisions that consider societal impacts
- Systems Thinking: Understanding how complex systems interact and influence each other
The New Work Paradigm: Human-AI Collaboration
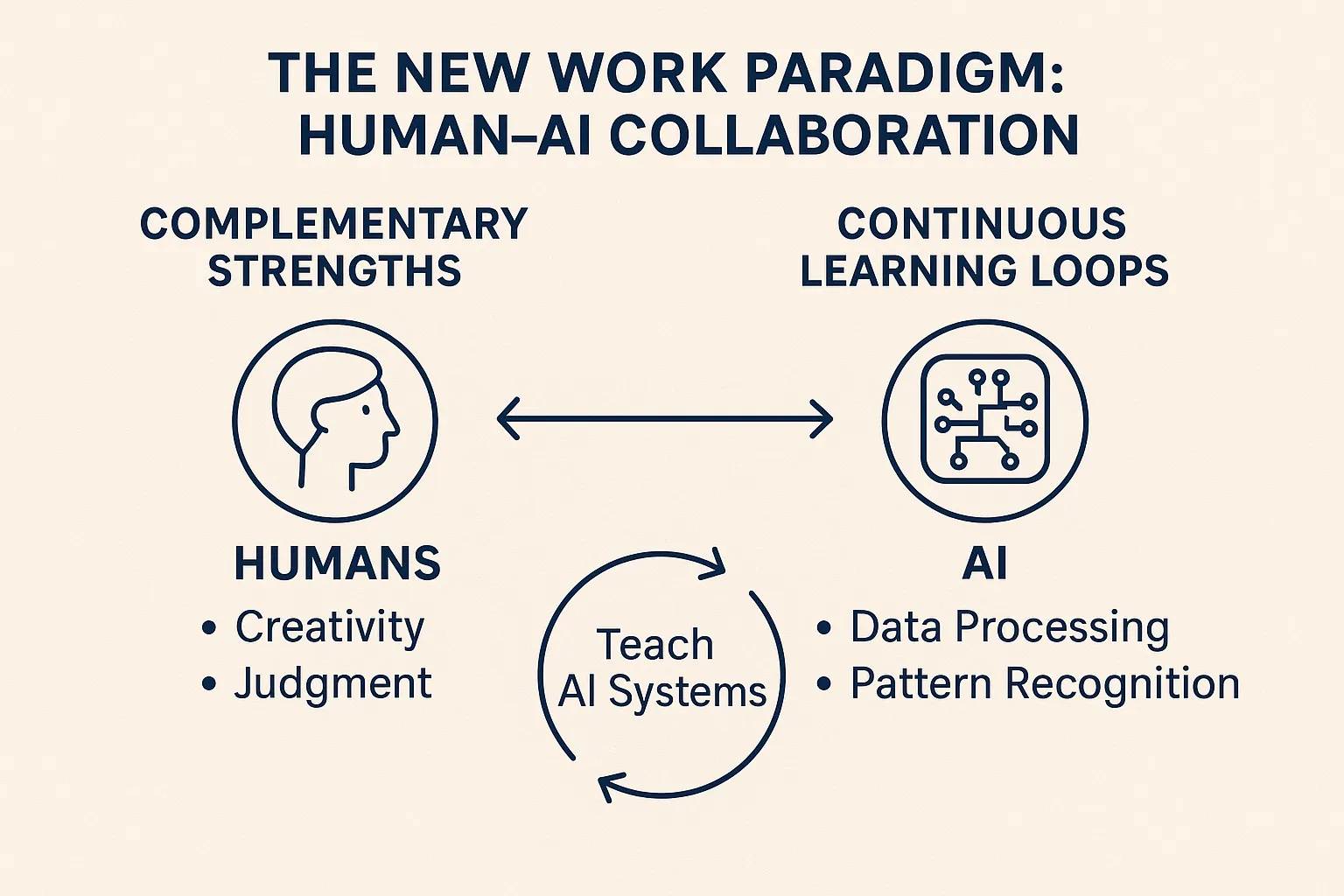
The most successful businesses in 2030 won't be choosing between humans or AI—they'll be mastering human-AI collaboration:
- Complementary strengths: Humans providing creativity and judgment, AI handling data processing and pattern recognition
- Augmented intelligence: AI systems enhancing human capabilities rather than replacing them
- Continuous learning loops: Humans teaching AI systems, which then provide insights that humans learn from
"The question isn't whether AI will replace jobs, but how we redesign jobs in an age of AI." — Daniela Rus, Director, MIT Computer Science and AI Laboratory
Industry-Specific Impacts of AI Agents
Different sectors will experience AI transformation at different rates and in different ways:
Healthcare
- High automation potential: Medical record management, appointment scheduling, basic diagnostics
- Low automation potential: Complex diagnoses, empathetic patient care, surgical procedures
- Emerging hybrid roles: AI-assisted diagnosticians, telemedicine specialists, medical data interpreters
Financial Services
- High automation potential: Transaction processing, basic customer service, regulatory reporting
- Low automation potential: Complex financial advisory, relationship management, novel financial product design
- Emerging hybrid roles: Algorithm risk managers, AI-augmented advisors, financial data ethicists
Manufacturing
- High automation potential: Assembly line operations, quality control, inventory management
- Low automation potential: Complex maintenance, custom fabrication, production innovation
- Emerging hybrid roles: Human-robot collaboration specialists, advanced manufacturing designers
Retail
- High automation potential: Checkout processes, inventory tracking, basic customer support
- Low automation potential: Personalized shopping experiences, complex customer problem-solving
- Emerging hybrid roles: Experience designers, AI-enhanced personal shoppers, omnichannel orchestrators
Preparing Your Business for the AI Transition
Strategic Planning for AI Integration
- Audit current workflows to identify automation opportunities
- Map employee skills against future needs
- Develop phased implementation plans for AI adoption
- Create reskilling pathways for affected employees
- Design new organizational structures that optimize human-AI collaboration
Building an AI-Ready Workforce
For business leaders, preparing your team for AI integration requires:
- Skills assessment: Identifying which employees have adaptable skill sets
- Learning culture: Establishing continuous education as a core value
- Cross-training: Developing versatility across multiple domains
- Soft skills development: Emphasizing uniquely human capabilities
Ethical Considerations in AI Deployment
As you implement AI agents, consider:
- Transparency: Can employees and customers understand how AI decisions are made?
- Accountability: Who is responsible when AI systems make mistakes?
- Bias prevention: How will you ensure AI systems don't perpetuate existing biases?
- Privacy protection: What data governance frameworks will protect sensitive information?
🔮 The Future Workplace: Scenarios for 2030

Scenario 1: The Augmented Workforce
In this future, most workers collaborate with AI agents that handle routine aspects of their roles. Productivity increases dramatically, and work focuses on uniquely human contributions. New jobs emerge to manage AI systems and address complex challenges.
Scenario 2: The Bifurcated Economy
This scenario sees a growing divide between those who can work effectively with AI and those who cannot. Companies that invest in workforce transition succeed, while others face talent shortages and competitive disadvantages.
Scenario 3: The Human Renaissance
As AI handles routine work, human roles emphasize creativity, empathy, and wisdom. Work becomes less about processing information and more about applying judgment, creating meaning, and building relationships.
Case Studies: AI Agents in Action Today
Acme Manufacturing: Collaborative Robotics
Acme implemented collaborative robots that work alongside human employees, handling repetitive tasks while humans manage exceptions and quality control. The result: 40% productivity increase without workforce reduction.
Horizon Financial: AI-Augmented Advisors
Horizon equipped financial advisors with AI assistants that handle research, documentation, and basic client communications. Advisors now serve 30% more clients while providing more personalized service.
GreenLeaf Retail: Intelligent Operations
GreenLeaf deployed AI agents for inventory management, demand forecasting, and basic customer service. Store associates shifted focus to personalized shopping experiences, increasing both sales and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion: Navigating the AI Transition
Will AI agents replace human workers by 2030? The evidence suggests a more nuanced outcome than wholesale replacement. The future belongs to businesses that can:
- Strategically implement AI in areas where it delivers clear value
- Redesign work processes to optimize human-AI collaboration
- Invest in employee transition through reskilling and role evolution
- Create organizational cultures that embrace technological change
The $7 trillion question isn't really about replacement—it's about transformation. The businesses that thrive won't be those that simply automate jobs away, but those that reimagine work itself, creating new value through the powerful combination of human creativity and artificial intelligence.
The future of work isn't human OR machine. It's human AND machine, working together in ways we're just beginning to discover.
Your Next Steps
- Conduct an automation readiness assessment for your business
- Identify high-potential areas for AI agent implementation
- Develop a skills transition roadmap for your workforce
- Explore AI tools that complement rather than replace your team's capabilities
- Start small experiments with AI augmentation in low-risk areas